Welcome to the first part of the AGIX Cybersecurity training course. This course is focused on staff related matters. Cybersecurity relates to people as much as organisations, and as such we’ll ensure home and work perspectives are covered. We discuss the methods and solutions, and we discuss what to look out for.
Scammers are the biggest threat to staff. Anyone can be scammed.
Table of Contents
Targets
- Everyone is a target:
- Businesses.
- Individuals.
Objectives of criminals
- Identity theft (which leads to),
- Financial gain.
Methods
- Phishing emails and phone calls:
- Sometimes forged phone numbers.
- Sometimes real phone numbers.
- Fake websites:
- Story about website cloning combined with phishing emails.
- Access to email and social media.
- In person interactions:
- Site visits.
- Door to door. (opportunistic)
- Coffee shop.
- Common scams to be aware of:
- Over payment scams.
- Late bill scams.
- Account cancellation scams.
- Story about gift-card scams.
- Opportunity scams.
- New ideas.
- Product import.
- Story about import scams.
- Work from home.
- High pay for low effort.
- Emotional attack:
- Start of as normal relatable interactions.
- Commonalities such as work focus.
- Work status.
- Living city.
- Offers to solve financial problems.
Exposure points
- Email.
- SMS.
- Social media.
- Phone.
- Mail (post).
- Office (visit).
- Home (visit).
Solutions
- Verify visitors:
- Site visits are common.
- Assume untrusted before trusted.
- Checks and balances:
- Involve multiple people if unsure/new/suspicious.
- Ensure multiple people are involved in impacting matters.
- Patching (install the latest updates):
- Patch Windows (home and at work).
- Patch Web Browsers (Firefox, Chrome, Edge, etc).
- Patch Android phones and tablets (Samsung Galaxy, Pixel, etc).
- Patch iPhones and iPads.
- Secure online:
- Ensure websites are “https://”.
- Ensure websites are “real”.
- Use a “password manager” and/or your web browsers built-in password manager.
- Verify contact details in emails (including the footer).
- Verify the true identify of callers (phone, SMS).
- Backup important information:
- Keep copies of important data in two physically different locations.
- Wherever information is kept, ensure access is restricted.
- Keep passwords safe:
- Use a password manager.
- Don’t share passwords with anyone.
- Change passwords regularly.
- Set requirements based on risk:
- Require additional checks if thresholds are met or exceeded.
- 2FA:
- If a system allows 2FA, use it.
- It’s very effective.
- Authentication Apps are the best form.
- Email is a less acceptable form.
- SMS is the weakest form.
- Strong passwords:
- Use complex and meaningful passwords.
- Unique passwords:
- Don’t reuse passwords for different systems/services (social media, email, work).
- Incident reporting:
- Can be embarrassing.
- Protect your email accounts at all costs:
- Email is a recovery system.
- Email holds sensitive information.
Example Email
The following two images are real emails received. One is a legitimate, while the other is now.

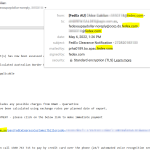
Resources
- https://www.scamwatch.gov.au/types-of-scams